Individual Mindsets vs. Collective Mindsets
Individual Mindsets vs. Collective Mindsets
We often talk about the need for individuals to change their mindsets – their assumptions, beliefs, and attitudes – in order to create positive change. But as human beings, we don’t exist in isolation. As the saying goes, we are social animals, shaped by the groups and cultures we are part of. So perhaps we might choose rather to shift more of our focus to addressing collective mindsets rather than just individual ones.
Schein On
Organisational psychologist and author Edgar Schein argues that culture stems from a group’s shared basic assumptions and beliefs. These collective ways of thinking and being manifest in organisational policies, processes and behaviors. If the culture has dysfunctional aspects, it perpetuates dysfunction. Merely helping individials adopt more productive mindsets without addressing the surrounding culture is an uphill battle.
For Example
Take a common example – trying to promote more innovative thinking in a risk-averse bureaucratic workplace. Telling individuals to “be more innovative” often backfires. When people attempt new ways of doing things, they get pushback for not following protocols. and Interesting ideas get shut down quickly by naysayers. There are no systems or incentives to support innovation. So you end up with frustrated employees, not actual innovation.
Organisational Psychotherapy To The Rescue
In contrast, #OrganisationalPsychotherapy seeks to invite folks into uncovering and transforming collective assumptions and beliefs – the mental models that shape systems and culture. By facilitating more awareness of existing culture and defining desired culture, interventions get better traction. Collective mindsets shift to be more supportive of stated goals, like innovation, making it easier for individuals to adopt those productive mindsets as well.
Summary
The key insight is that individual mindsets are downstream of collective mindsets. Without addressing dysfunctional aspects of culture and systems, individual change efforts face resistence from the surrounding ecosystem. This highlights the need to focus on group mindset factors first and foremost. Of course, individuals still have agency in driving any kind of change. But we’d do well to spend more time examining and evolving the shared beliefs and assumptions on which any organisation is built. For cultural transformation, that’s likely the most high-leverage point of intervention.
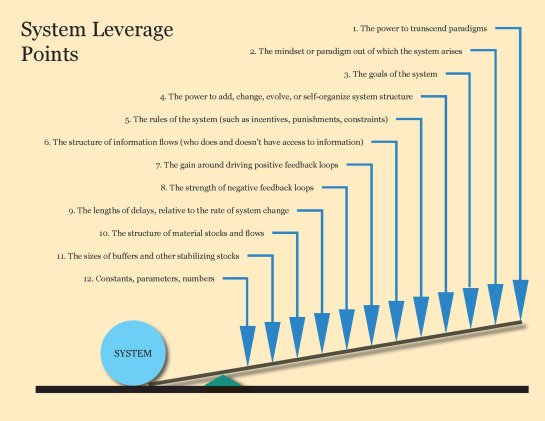
Postscript – Donalla Meadows’ Twelve Points of Leverage
In her influential article “Leverage Points: Places to Intervene in a System,” systems thinker Donella Meadows articulated 12 places within complex systems where a small shift can lead to fundamental changes in the system as a whole. Her framework offers guidance on how to approach system-level transformation, whether in organizations, societies, or beyond.
Meadows proposes 12 leverage points ranked in order of effectiveness, with the most high-leverage interventions at the top. The higher the leverage point, the easier it is to make major improvements to the system with minimal effort. Her list starts with more superficial leverage points around details like subsidies and incentives, then moves deeper into the fundamental goals, paradigms, and transcending purpose that underpin why a system exists in the first place.
The most powerful leverage points require a deeper, more courageous transformation. But they allow us to redefine the very reason a given system exists, enabling revolutionary redesign rather than incremental improvements. Meadows urges change agents to have the wisdom and patience to address the deeper paradigms, values, and purpose driving systemic behavior. As she concludes, “People who have managed to intervene in systems at the level of paradigm have hit a leverage point that totally transforms systems.”
In examining Meadows’ hierarchy of leverage points, we gain an appreciation for the depth of change required for true systems transformation. It inspires a more radical reimagining of what’s possible. The framework continues to provide guidance to sustainability leaders and organizational change agents seeking to effect large-scale improvements in business, government, technology, education and beyond. In this critical era facing many complex, planetary-scale challenges, Meadows’ words ring truer than ever as we work to create fundamental shifts towards more just, resilient and life-affirming systems.